Key takeaways
Traditional AI analyzes data and supports decision-making, while generative AI creates new content like text, images, or code.
Generative AI is a subset of AI, not a separate technology.
Understanding the difference between AI vs generative AI helps law firms adopt the right tools for their needs.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and generative AI are two powerful branches of computer science that have become a normal component of our daily lives, with even law firms getting in on legal AI tools.
While both AI and generative AI are revolutionizing a range of industries, their functionalities differ greatly. Understanding these differences is paramount to leveraging their full potential.
In this article, you’ll discover the difference between AI and generative AI, where they overlap, and their limitations. We’ll also explore future advancements poised to propel AI even further.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) uses computer systems to mimic human intelligence and perform tasks. These systems rely on algorithms and data to make autonomous decisions, learn from previous experiences, and adapt to new situations. Traditional AI supports problem-solving, decision-making, and the automation of automating complex tasks by analyzing structured data.
In simpler terms, traditional AI excels at interpreting existing information, identifying trends, and making logical predictions. However, it doesn’t generate original ideas or content—that’s where generative AI comes in.
How Is AI Different From Traditional Computing?
To understand what makes AI unique, it helps to compare it with traditional computing. Traditional computing systems operate based on explicitly written code. Every decision they make must be predefined by a programmer. If "X" happens, the system does "Y."
AI, by contrast, doesn't need to be told exactly what to do in every scenario. Instead, it learns from large volumes of data, recognizes patterns, and adapts its behavior over time. This flexibility enables AI to handle more complex, variable problems where pre-programmed rules would fall short.
This adaptability allows AI to:
Learn from experience
Recognize complex patterns
Make predictions and decisions without being explicitly programmed
In short, traditional computing executes instructions; AI evolves and improves through learning.
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating new, original content. Rather than simply analyzing data or making predictions, generative AI models produce entirely new text, images, music, code, and more by learning patterns from vast training datasets.
What sets generative AI apart is its ability to synthesize novel outputs that resemble human-created content. These systems are trained using advanced techniques like deep learning, allowing them to understand language structure, image composition, and musical rhythm. Tools like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and others exemplify how generative AI shifts AI’s role from automation and analysis to creativity and content generation.
When Was Generative AI Invented?
Though generative AI has only become a hot topic in recent years, its foundation dates back to the development of early neural networks in the 1950s and 1960s, which laid the groundwork for machine learning and pattern recognition. Over the following decades, researchers built on these concepts with increasingly sophisticated models.
Practical applications of generative AI began to gain real momentum in the 2010s, thanks to breakthroughs in deep learning, access to large datasets, and increased computational power. The release of OpenAI's Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) models, starting with GPT-2 in 2019, followed by GPT-3 and GPT-4, marked a turning point in public and professional awareness.
By the early 2020s, tools like ChatGPT, Midjourney, and DALL·E brought generative AI into the mainstream. Today, it’s used across a wide range of industries—including law—to accelerate content creation, enhance communication, and increase productivity.
What Is the Difference Between AI and Generative AI?
While AI and Generative AI are distinct concepts, there are key differences between them. Traditional AI focuses on analyzing data and automating decision-making, whereas generative AI goes a step further, producing entirely new content like text, images, or code based on learned patterns.
Functionality
Traditional AI systems are built to execute specific tasks based on pre-defined rules and structured data. These tools are excellent at recognizing patterns, automating workflows, and making predictions—for instance, identifying fraud or recommending relevant documents.
Generative AI, however, is designed to produce entirely new content such as emails, contracts, or legal summaries. Rather than following fixed instructions, it draws on vast datasets to create outputs that mirror human-like creativity and language.
Key differences:
Traditional AI follows pre-defined rules to perform specific tasks.
Generative AI creates original content using learned data patterns.
Use Cases
Traditional AI systems are widely used to streamline operations, reduce repetitive work, and extract insights from large datasets. In the legal field, this includes tasks like predicting billing outcomes, classifying legal documents, or forecasting case results.
Generative AI, by contrast, unlocks new possibilities in content creation—drafting legal memos, generating marketing copy, or summarizing depositions. MyCase IQ uses generative AI to help law firms enhance their written communication and document summarization processes.
Key differences:
Traditional AI supports operational efficiency and decision-making.
Generative AI enables content creation and personalized communication.
Training Methods
The training process also distinguishes traditional AI from generative AI. Traditional AI systems are trained using supervised or unsupervised learning algorithms. Supervised learning involves training the system on labeled data—where the correct answers are provided—while unsupervised learning involves training the system on unlabeled data and allowing it to find patterns on its own.
Generative AI systems are trained using a technique called generative adversarial networks (GANs) or transformers. GANs use two networks to continuously improve the generated content:
A generator network creates new content (like text, images, or music).
A discriminator network evaluates the generated content and provides feedback to the generator network.
This iterative process of generating and evaluating content helps the generative AI system improve over time.
Key differences:
Traditional AI uses supervised/unsupervised learning with labeled data.
Generative AI uses self-supervised learning and models like GANs or transformers.
User Experience & Interaction
Users interact with traditional AI through defined interfaces such as dashboards, automated alerts, or rule-based systems. These systems are efficient and functional, but relatively static. Generative AI, in contrast, introduces a more dynamic, conversational experience where users guide the output through natural language prompts or iterative refinements. This collaborative interface makes prompt engineering and thoughtful input increasingly valuable for achieving optimal results.
Key differences:
Traditional AI offers structured, task-specific interfaces.
Generative AI relies on prompts and interactive refinement.
Core Users
Traditional AI is commonly used by analysts, legal researchers, and operations teams looking to automate repetitive processes and analyze large volumes of data. These users rely on AI to gain insights, improve decision-making, and boost efficiency.
Generative AI appeals to a broader range of users—including legal professionals, marketers, designers, and educators—who benefit from its creative and generative capabilities. Generative AI reshapes how professionals approach writing, communication, and ideation by allowing them to produce high-quality content more efficiently.
Key differences:
Traditional AI is used by data-focused roles (e.g., analysts, researchers).
Generative AI is embraced by creative and communication-centric professionals.
Examples of Common AI and Generative AI Tools
AI is already embedded in many of the tools professionals use every day—often without us even realizing it. From powering personalized playlists to streamlining legal workflows, both traditional and generative AI help improve efficiency and deliver smarter user experiences. Below are some widely used examples of how each type of AI shows up in common platforms.
Non-Generative AI Examples
Traditional AI excels at automation, pattern recognition, and decision support. These tools don’t generate content but instead improve accuracy, speed, and personalization by processing large volumes of data:
Google Search: Interprets user queries and ranks results using AI-powered relevance scoring.
Netflix / Spotify: Uses AI-based recommendation engines to suggest personalized content based on viewing or listening habits.
Tesla Autopilot: Employs AI and sensor data for driver assistance features such as lane keeping and adaptive cruise control.
HubSpot: Leverages AI for lead scoring, customer segmentation, and marketing automation to improve campaign targeting.
Generative AI Tools Examples
Generative AI tools are built to create new content—ranging from text and images to video and code—based on learned data patterns. These tools have quickly become essential for professionals across industries:
ChatGPT (OpenAI): A conversational assistant used for drafting legal documents, answering questions, and brainstorming content ideas.
Claude (Anthropic): A long-form chatbot designed to assist with detailed writing and complex reasoning.
Midjourney: An AI tool that transforms text prompts into artistic or photorealistic images, popular among creatives.
Microsoft Copilot: Embedded in Microsoft 365 apps, it generates emails, documents, and even code to boost productivity and reduce manual work.
Understanding Key Terminology Around AI and Generative AI
AI: An umbrella term for computer systems that mimic human intelligence to perform tasks.
Neural networks: A type of machine learning algorithm that mimics the structure and function of the human brain, allowing AI systems to learn and process complex data.
Machine Learning: A method that enables AI to improve performance over time by learning from data.
Deep Learning: A type of machine learning that uses layered neural networks to process complex data.
Generative AI: A subset of AI that focuses on creating original content such as text, images, or code.
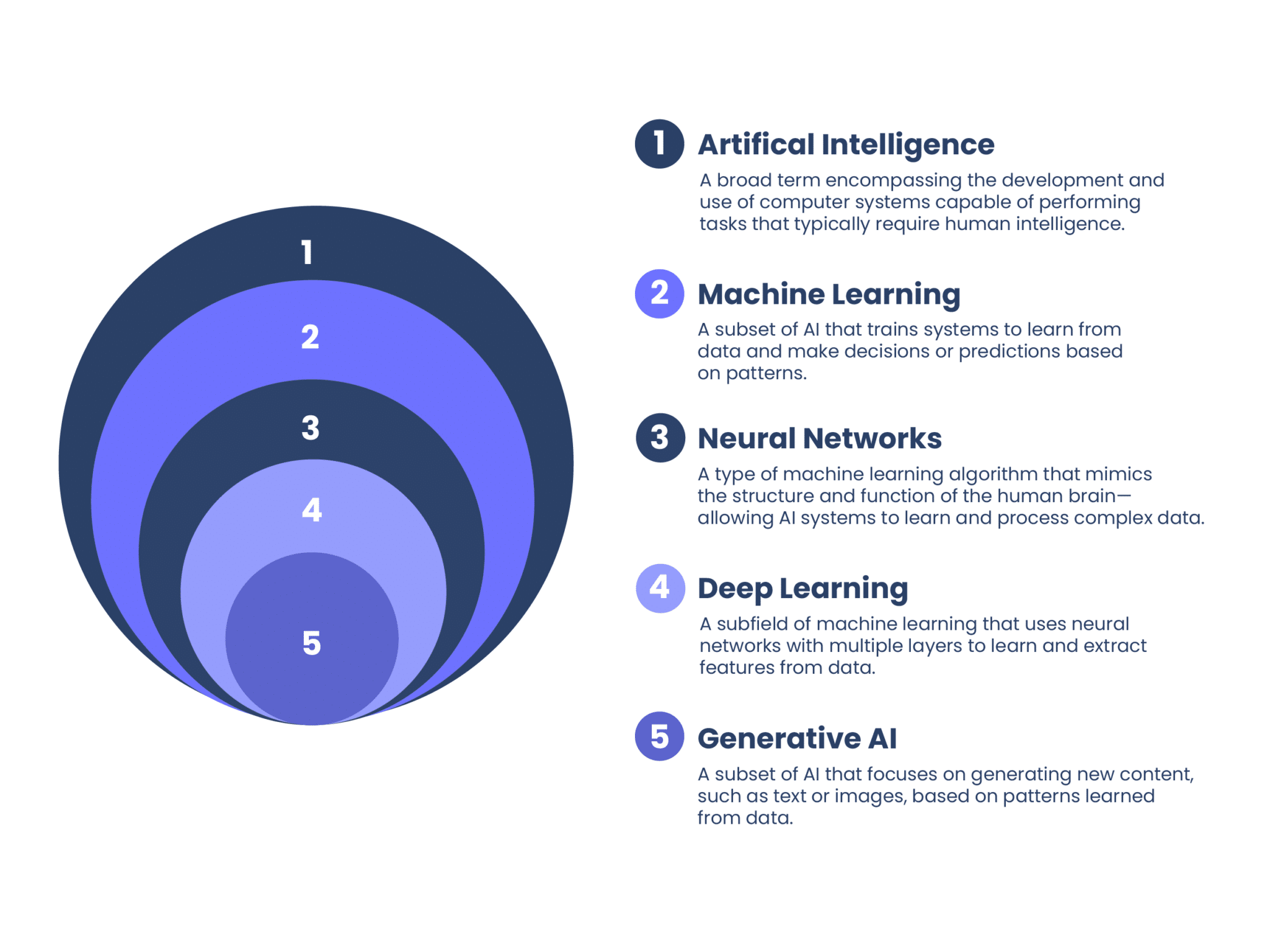
These concepts are deeply interconnected. Generative AI relies on machine learning—and more specifically, deep learning—to identify intricate patterns in massive datasets and use them to produce content that feels human-like.
What Are Some Limitations and Risks of AI and Generative AI?
As powerful as AI and generative AI can be, both technologies come with limitations and risks that professionals should carefully consider, especially in fields like law, where accuracy, fairness, and confidentiality are critical. Below are three key areas of concern:
Bias and Data Quality
AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If training datasets contain biases—such as skewed demographic representation or outdated legal precedents—those biases can influence the system's outputs. This is especially concerning in legal settings where impartiality is essential.
Transparency and Explainability
One of the most common criticisms of advanced AI systems, particularly generative models, is their "black box" nature. It can be difficult or even impossible to understand exactly how a system arrived at a specific decision or output. This lack of explainability makes it harder for legal professionals to fully trust the results or justify them in client communications.
Ethics and Client Confidentiality
Lawyers have an ethical obligation to protect client information. Using generative AI tools without proper safeguards could risk exposing confidential data, either through inadvertent input into public systems or unclear data-handling practices. Professionals must vet AI tools carefully to ensure they align with legal and ethical standards.
Understanding these challenges is essential to using AI responsibly. By approaching both traditional and generative AI with clear guidelines and a focus on quality and security, legal professionals can reduce risk and increase the reliability of their tools.
The Future of AI in the Professional Industries
The world of AI is vast and ever-evolving. While traditional AI excels at analyzing data and automating tasks, generative AI adds a revolutionary twist by creating entirely new content. Understanding the difference between AI and generative AI is crucial to effectively navigating this rapidly developing field.
As for what’s next, a convergence between the two is only a matter of time. By leveraging the unique capabilities of each system, more powerful and innovative solutions are bound to emerge. It will no longer be a question of traditional AI vs generative AI, but instead, a focus on harnessing their synergy.
The legal field is a prime example of an industry ripe for AI-powered innovation. Legal professionals can leverage generative AI for tasks like document review, contract analysis, and legal research. Lawyers can use ChatGPT and other AI tools to free up valuable time to focus on legal issues and client strategy. There are several benefits of AI for lawyers, and these tools provide a glimpse into the exciting future of legal AI technology.
Why Lawyers Should Care About AI
Whether you’re managing a firm or drafting contracts, understanding AI vs generative AI ensures you choose tools that enhance productivity without compromising security. Tools like
MyCase IQ integrates generative AI directly into your workflow, helping you:
Summarize discovery documents
Draft and refine legal text
Capture billable time with Smart Time Finder
Learn more about MyCase IQ or schedule a demo.
FAQs Related to AI and Generative AI
About the author

Gabriela JheanContent Writer
Gabriela Jhean is a Content Writer for leading legal software companies, including MyCase, Docketwise, and CASEpeer, as well as LawPay, the #1 legal payment processor. She covers emerging legal technology, financial wellness for law firms, the latest industry trends, and more.
